
|
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
One approach for valuing inventory is the average cost method, which determines the cost of each item in inventory by dividing the total cost of products bought or produced over a certain period by the total number of things bought or produced.
To calculate the average cost per unit, the following formula is used:
Average cost per unit = Total cost of goods available for sale / Total units available for sale
The total cost of goods available for sale is the sum of the beginning inventory cost and the purchases or production cost during the period. The total units available for sale are the sum of the beginning inventory units and the purchases or production units during the period.
To calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS) using the average cost method, the following formula is used:
COGS = Average cost per unit x Units sold
The COGS is an important figure for businesses, investors, and analysts as it is subtracted from sales revenue to determine gross margin on the income statement.
To calculate the ending inventory value using the average cost method, the following formula is used:
Ending inventory value = Average cost per unit x Units in ending inventory
The ending inventory value represents the cost of goods that are still available for sale at the end of the period.
Let's look at an example of how to apply the average cost method. Suppose a company sells widgets and has the following inventory transactions in January:
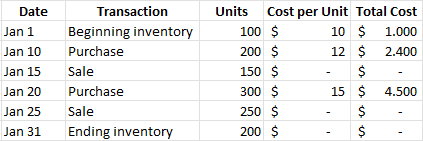
|
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
To calculate the average cost per unit, we need to add up the total cost of goods available for sale and divide it by the total units available for sale.
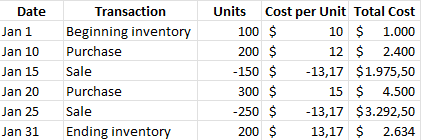
Total cost of goods available for sale = $1,000 + $2,400 + $4,500 = $7,900
Total units available for sale = 100 + 200 + 300 = 600
Average cost per unit = $7,900 / 600 = $13.17
To calculate the COGS for each sale, we need to multiply the average cost per unit by the units sold.
COGS for Jan 15 sale = $13.17 x 150 = $1,975.50
COGS for Jan 25 sale = $13.17 x 250 = $3,292.50
Total COGS for January = $1,975.50 + $3,292.50 = $5,268
To calculate the ending inventory value, we need to multiply the average cost per unit by the units in the ending inventory.
Ending inventory value = $13.17 x 200 = $2,634
The following table summarizes the results of applying the average cost method:
|
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
