 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
Asset valuation is the process of figuring out the fair market worth of an asset, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or commodities. Because it has an impact on resource allocation, risk and return assessment, and adherence to accounting rules and regulations, asset valuation is significant to investors, businesses, and regulators.
There are different methods and approaches for asset valuation, depending on the type, purpose, and context of the asset. Some of the common methods are:
- Market approach: This approach calculates the asset's worth using the market values of comparable or related assets. For instance, by examining the costs of comparable homes in the same neighborhood or region, one might determine the value of a house.
- Income approach: This approach calculates the asset's present value using the anticipated future cash flows or income it will produce. A bond's value, for instance, can be calculated by applying a suitable interest rate to future coupon payments and principal repayment.
- Cost approach: This method uses the cost of creating or replacing the asset to estimate its value. For example, the value of a machine can be estimated by adding up the costs of labor, materials, and overheads involved in its production or acquisition.
- The asset's attributes and qualities, including its nature, maturity, liquidity, riskiness, cash flow structure, etc.
- The valuation's purpose and context, including whether it is being done for investments, reporting, taxes, regulations, etc.
- Data and information about the asset and its market, including historical prices, volumes, trends, and projections, are both readily available and of high quality.
- the methods and assumptions used to project the asset's future cash flows or income, including growth rates, discount rates, inflation rates, etc.
- Changes in inputs and assumptions are a result of the valuation's sensitivity and uncertainty.
Stock Valuation
Let's attempt valuing the New York Stock Exchange-listed company BlackRock (NYSE: BLK). BlackRock's market value was $96.52 billion as of September 30th, 2023, and its share price was $910.
 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
These ratios were used to construct an average relative valuation multiple for BlackRock's shares using a weighted average of its peers' multiples. For example,
 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
The estimated fair value per share of BlackRock was then calculated by multiplying this average multiple by the company's profits per share (EPS), book value per share (BVPS), or sales per share (SPS). For example,
The average fair value per share based on these three multiples is $744.
To calculate BlackRock's intrinsic value per share for the income approach, utilize a discounted cash flow (DCF) model based on the company's anticipated future free cash flows (FCF). Using historical growth rates, margins, and capital expenditure data, BlackRock's FCF was projected for the following five years. For example,
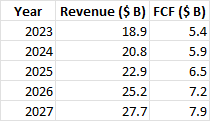 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC), which represents BlackRock's minimum acceptable rate of return for its investors, is then applied to these FCFs. Based on its capital structure, cost of debt, and cost of equity, BlackRock's WACC is projected to be 8%. For example,
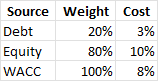 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
The enterprise value (EV), which is the total value of BlackRock's business, is calculated as the present value of FCF plus terminal value. Subtract BlackRock's net debt (total debt less cash and equivalents) from its EV to obtain the equity value. Divide the equity value by the number of outstanding shares to find the fair value per share. For example,
 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
The average fair value per share based on the market approach and the income approach is $800.
Real Estate Valuation
For the real estate properties let's try to value a commercial office building located in New York City. The property has a total area of 500,000 square feet, with an occupancy rate of 90% and an average rent of $50 per square foot per year.Both market and income approaches should be used to appraise this property. In the case of the market method, valuation metrics for the property (such as price per square foot, capitalization rate, etc.) were compared to those of comparable properties in the same market or region. For example,
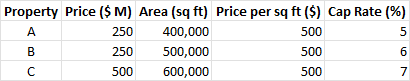 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
Calculate an average relative valuation multiple for the property based on these characteristics by averaging the multiples of its competitors. For example,
 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
To determine the property's estimated fair value, multiply this average multiple by the area or net operating income (NOI) of the building. For example,
 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |
The average fair value based on these two multiples is $237.5 million.
To calculate the property's intrinsic value using the income approach, apply a discounted cash flow (DCF) model based on the anticipated net operational income for the property in the future (NOI). This can be accomplished by estimating the property's NOI over the course of the following ten years using its historical occupancy rate, rent growth rate, and operating expense data. For example,
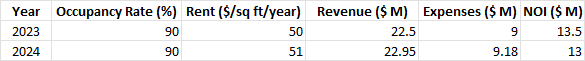 |
| Image: Moneybestpal.com |


